FirstDuct Material Comparison
- Size
- Air Tight
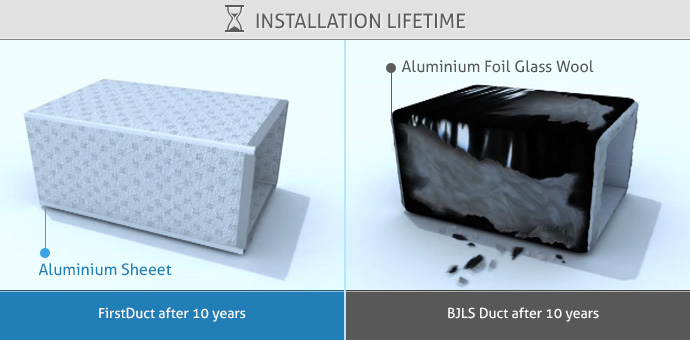
- Installation Lifetime
- Air Quality
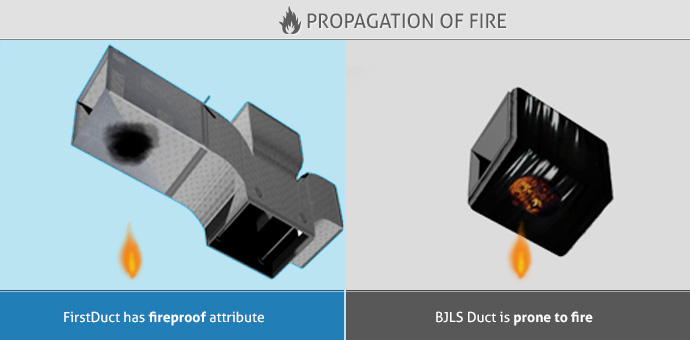
- Propagation of Fire
- Ducting Making
- Aesthetics
- Maintenance
- Price
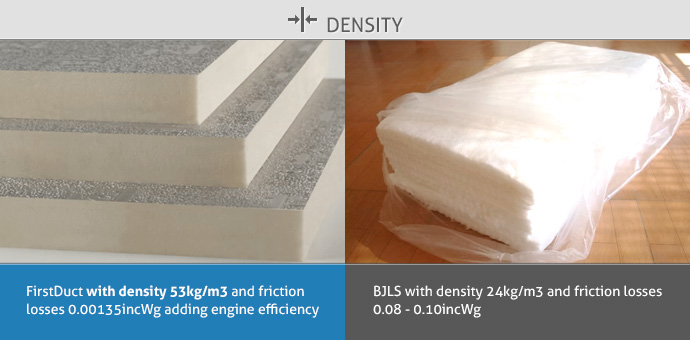
- Density
- Weight
Compare

Comparison
First Duct panel product is the preferred solution for all your ducting needs. Here on this spread we compare the different types of ductings compared to that of ours.
| FirstDuct Panels | Flexible Ducts | Spiral Sheet Metal | Rectangural Sheet Metal |

|

|

|

|
| PERFORMANCE |
| Thermal insulation |
| Air seal |
| Friction loss |
| Acoustics |
| Air quality and hygiene |
| Lifespan |
| Safety |
| Transport |
| Construction |
| Installation |
| Availability |
| Easy estimation |
| Competitiveness |
| Energy saving |
Leaking Air
| Static pressure within the duct (Pa) | First Duct wind leakage Volume (1/s.m2) | Metal Sheet wind leakage Volume (1/s.m2) |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | 0.083 | 0.7636 |
| 400 | 0.134 | 1.2328 |
| 1000 | 0.44 | 4.048 |
| 2000 | 0.801 | 7.3692 |
Energy Saving
| Material | Energy saving index |
|---|---|
| 20 mm First Duct with thermal insulation | 85.23% |
| 25 mm duct from galvanizing iron sheet | 79.14% |
| 19 mm duct from galvanizing iron sheet | 74.26% |
| 8 mm duct from galvanizing iron sheet | 59.51% |
| Duct from galvanizing iron sheet | 0 |
R-Value
| Insulation Materials | R / Inch |
|---|---|
| Fiberglass Batt | 3.14 - 4.30 |
| Fiberglass Blown (attic) | 2.20 - 4.30 |
| Fiberglass Blown (wall) | 3.70 - 4.30 |
| Rock Wool Batt | 3.14 - 4.00 |
| Rock Wool Blown (attic) | 3.10 - 4.00 |
| Rock Wool Blown (Wall) | 3.10 - 4.00 |
| Cellulose Blown (attic) | 3.13 |
| Cellulose Blown (Wall) | 3.70 |
| Vermiculite | 2.13 |
| Autoclaved Aerated Concrete | 1.05 |
| Urea Terpolymer Foam | 4.48 |
| Rigid Fiberglass ( > 4lb/ft3) | 4.00 |
| Expanded Polystyrene (beadboard) | 4.00 |
| Extruded Polystyrene | 5.00 |
| Polyurethane (foamed-in-place) | 6.25 |
| Polyisocyanurate (foil-faced) | 7.20 |
The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance used in the building and construction industry. Under uniform conditions it is the ratio of the temperature difference across an insulator and the heat flux (heat transfer per unit area per unit time, 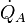 ) through it or
) through it or  . Thermal resistance varies with temperature but it is common practice in construction to treat it as a constant value.
. Thermal resistance varies with temperature but it is common practice in construction to treat it as a constant value.
An R-value is a unit thermal resistance for a particular material or assembly of materials (such as an insulation panel). The R-value depends on a solid material's resistance to conductive heat transfer. For loose or porous material, the R-value accounts for convective and radiative heat transfer through the material. However it does not acocunt for the radiative or convective properties of the materials surface, which may be an important factor for some applications.
R is expressed as the thickness of the material normalized to the thermal conductivity. The unit thermal conductance of a material is the reciprocal of the unit thermal resistance. This can also be called the unit surface conductance. The higher the number, the better the building insulation's theoretical effectiveness.